ai-sdk
1.14.17- How it works
- Getting Started
- Modules
- ADVANCED TOPICS
- Troubleshooting
- Requirements
- Change Log
- Code interface
- loader
- modules
-
createSource
▸
- Static members
- .fromCamera
- .fromVideoElement
- .fromVideoUrl
-
AiSdkBuilder
▸
- Instance members
- #addModule
- #powerSave
- #source
- #maxInputFrameSize
- #loadErrorHandler
- #runErrorHandler
- #busyHandler
- #load
- Camera ▸
How it works
First step: get your full features licence for free:  MorphCast HTML5 AI SDK is a native JavaScript engine, based on Deep Neural Networks.
MorphCast HTML5 AI SDK is a native JavaScript engine, based on Deep Neural Networks.
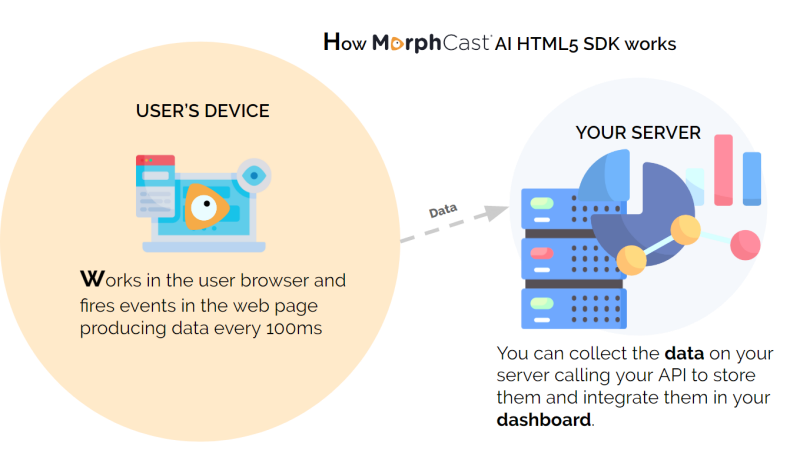
It works directly in the web-browser of mobile and desktop and in a webview inside mobile App.
It fires events at an average rate of 10 times per second on mobile, and even up to 30 per second on desktop.
Data output is ready-to-use, already filtered for your convenience (parameters can also be changed in order to have a smoother or RAW output for more deep use in your code).
You can store all data produced in local memory, in local storage or properly send it to your server.
This SDK was developed with you in mind, to have a really quick integration into your application.
Getting Started
By proceeding to use MorphCast HTML5 AI SDK, you agree to our Terms of Use.
Usage (including alert plugin)
Copy and paste the following code snippet inside an HTML page:
<head>
...
<meta name="mphtools-feature" content="compatibilityUI, cameraPrivacyPopup, compatibilityAutoCheck">
</head>
<body>
...
<script src="https://sdk.morphcast.com/mphtools/v1.0/mphtools.js"></script>
<script src="https://ai-sdk.morphcast.com/v1.14/ai-sdk.js"></script>
<script>
CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load()
.then(({ start, stop }) => start());
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face detector result', evt.detail);
});
</script>
...
</body>
It already includes automatic alerts about browser and App compatibility:
- general incompatibility alert if the browser does not support the camera,
- privacy alert when requesting camera permit,
- warning if the user has denied access to the camera,
- incompatibility alert related to Facebook / Instagram / Linkedin and WeChat Apps which invites you to open with Safari (for iOS) or with Chrome (for Android),
- invite to re-open the page with Safari in case of other iOS browser (not compatible).
Usage (SDK without alert plugin)
Copy and paste the following code snippet inside the body of an HTML page.
<body>
...
<script src="https://ai-sdk.morphcast.com/v1.14/ai-sdk.js"></script>
<script>
CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load()
.then(({ start, stop }) => start());
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face detector result', evt.detail);
});
</script>
...
</body>
A trial license is automatically generated at the first usage. You shall serve the web page file using a web server, remote or local (e.g. http://localhost).
Since camera access requires https, when using a private network ip (e.g. https://192.168.x.x) or a public domain, you shall enable SSL in your web server configuration.
The SDK will automatically open and manage a camera stream internally, as well as the browser camera request.
Modules
Below, a list of available modules. You can combine them as you like, e.g. to load FACE_DETECTOR and FACE_AGE:
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name, {})
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_AGE.name, {})
FACE_DETECTOR
FACE_DETECTOR initialization:
const config = {maxInputFrameSize: 320, multiFace: false};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name, config)
-
config:
- maxInputFrameSize: Number, default 320 (pixel). Reduces input dimensions to the maximum specified size, before performing face detection. Input dimensions should be greater or equal, up-scaling is not allowed. Normally, the value set should be between 160 and 640.
- multiFace: Boolean, default false. Enables multi-face detection, i.e. allows to detect more than one face. It can slow down performance on lower-end devices, since the face tracker will be disabled and a full detection will occur for each frame.
FACE_DETECTOR registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face detector result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_DETECTOR event.detail:
const FACE_DETECTOR_EVENT = {
faces: Array(n),
rects: Array(n),
status: String,
fullFrameDetection: Boolean,
totalFaces: Number,
totalFacesChangedFrom: Number | undefined
}
- faces: An array containing the detected faces in form of ImageData objects (zero or one; or multiple faces, if fullFrameDetection is true)
-
rects: An array of objects describing the bounding boxes (zero or one; or multiple rects, if fullFrameDetection is true)
- x: The upper left point x coordinate
- y: The upper left point y coordinate
- width: The width of the bounding box
- height: The height of the bounding box
-
status: A string containing the status of the face tracker
- "INIT": Tracker is initializing; zero or many faces could be returned
- "TRACK_OK": Tracker is correctly tracking one face; one face is returned
- "RECOVERING": Tracker has lost a face and is attempting to recover and continue tracking; zero faces are returned
- fullFrameDetection: A boolean. It is true when detection was full-frame and multiple faces can be returned, false otherwise.
- totalFaces: A number. It represents the total number filtered of faces detected, smoothened over an interval of time. By default, one face is the maximum number. If multi-face is enabled, the maximum is 6. This output is not synchronized with faces and rects arrays, do not use it to count their lengths!
- totalFacesChangedFrom: Optional, a number. When there is a significant change in the number of faces, it is defined and represents the previous number of faces. In case no change occurred, it is undefined. This output is not synchronized with faces and rects arrays.
Note: if you ever notice some false positives in the events, i.e. the face is detected as present even if there is no one, you can further filter the results by the confidence property of the elements contained in the rects array (e.g. rects[0].confidence > 10)
Example
For detecting face presence, you can use the following snippet:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, (evt) => {
if(evt.detail.totalFacesChangedFrom !== undefined) {
console.log('Number of faces changed. Was: ' + evt.detail.totalFacesChangedFrom + ' . Now is: ' + evt.detail.totalFaces);
}
});
FACE_POSE
FACE_POSE initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.65};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_POSE.name, config)
-
config:
- smoothness: Number, default 0.65. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response. Set it to 0 (zero) if you need the raw signal.
FACE_POSE registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_POSE.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face pose result', evt.detail);
});
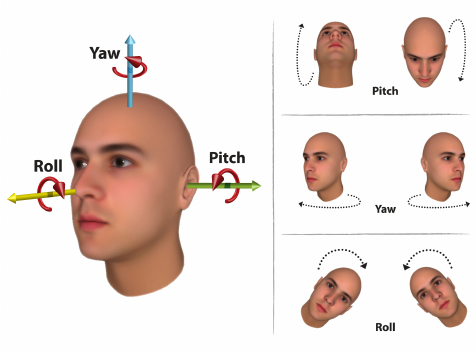
FACE_POSE event.detail:
const FACE_POSE_EVENT = {
output: {pose: {pitch: Number, roll: Number, yaw: Number}}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the pose prediction
- pose: An object containing the filtered (smoothened) pose rotation angles expressed in radians as pitch, roll and yaw.
FACE_AGE
FACE_AGE initialization:
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_AGE.name, {})
FACE_AGE registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_AGE.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Age result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_AGE event.detail:
const FACE_AGE_EVENT = {
output: {age: {_-18: Number, 18-35: Number, 35-51: Number, 51-_: Number}, numericAge : Number}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the age prediction
-
age: An object containing the probabilities of the filtered (smoothened) age prediction:
- _-18: The probability that predicted age is less than 18 years old.
- 18-35: The probability that predicted age is greater than or equal to 18 years old and less than 35 years old.
- 35-51: The probability that predicted age is greater than or equal to 35 years old and less than 51 years old.
- 51-_: The probability that predicted age is greater than or equal to 51 years old.
- numericAge: A numeric estimate for the age
-
Note: in case of poor quality of the prediction, by default, the event is not fired (i.e. skipped for that frame).
FACE_EMOTION
FACE_EMOTION initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.40, enableBalancer : false};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_EMOTION.name, config)
-
config:
- enableBalancer: Boolean, default false. Experimental filter able to adjust emotions, according to the emotional baseline of each person.
- smoothness: Number, default 0.40. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response. Set it to 0 (zero) if you need the raw signal.
FACE_EMOTION registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_EMOTION.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Emotion result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_EMOTION event.detail:
const FACE_EMOTION_EVENT = {
output: {
dominantEmotion: String,
emotion: {Angry: Number, Disgust: Number, Fear: Number, Happy: Number, Neutral: Number, Sad: Number, Surprise: Number}
}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the emotion prediction
- dominantEmotion: the name of the dominant emotion if present, otherwise it is undefined.
-
emotion: An object containing the filtered (smoothened) values of the probability distribution of emotions. The sum of all the probabilities is always 1, each probability in the distribution has a value between 0 and 1.:
- Angry: The probability for Angry.
- Disgust: The probability for Disgust.
- Fear: The probability for Fear.
- Happy: The probability for Happy.
- Sad: The probability for Sad.
- Surprise: The probability for Surprise.
- Neutral: The probability for Neutral.
FACE_GENDER
FACE_GENDER initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.95, threshold: 0.70};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_GENDER.name, config)
-
config:
- smoothness: Number, default 0.95. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response. Set it to 0 (zero) if you need the raw signal.
- threshold: Number, default 0.70. Value should be in range [0.5,1). It controls the minimum value of confidence for which mostConfident output returns the predicted gender name instead of undefined.
FACE_GENDER registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_GENDER.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Gender result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_GENDER event.detail:
const FACE_GENDER_EVENT = {
output: {mostConfident: String}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the gender prediction
-
mostConfident: Gender name ("Male" or "Female") of the most likely result if its smoothened probability is above the threshold, otherwise it is undefined.
-
FACE_FEATURES
FACE_FEATURES initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.90};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_FEATURES.name, config)
-
config:
- smoothness: Number, default 0.90. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response. Set it to 0 (zero) if you need the raw signal.
FACE_FEATURES registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_FEATURES.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face features result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_FEATURES event.detail:
const FACE_FEATURES_EVENT = {
output: {features: {Arched Eyebrows: Number, Attractive: Number, ...}}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the face features prediction
-
features: An object containing the filtered (smoothened) probabilities of each face independent feature in range [0.0, 1.0]:
Arched Eyebrows Attractive Bags Under Eyes Bald Bangs Beard 5 O'Clock Shadow Big Lips Big Nose Black Hair Blond Hair Brown Hair Chubby Double Chin Earrings Eyebrows Bushy Eyeglasses Goatee Gray Hair Hat Heavy Makeup High Cheekbones Lipstick Mouth Slightly Open Mustache Narrow Eyes Necklace Necktie No Beard Oval Face Pale Skin Pointy Nose Receding Hairline Rosy Cheeks Sideburns Straight Hair Wavy Hair
-
FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE
FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.70};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE.name, config)
-
config:
- smoothness: Number, default 0.70. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response. Set it to 0 (zero) if you need the raw signal.
FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face arousal valence result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE event.detail:
const FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE_EVENT = {
output: {
calibrated: { arousal: Number, valence: Number },
affects38 : { "Afraid": Number, "Amused": Number, .. },
affects98 : { "Adventurous": Number, "Afraid": Number, .. },
quadrant : String
}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the face arousal/valence prediction
-
calibrated: An object containing the smoothened arousal/valence values.
- arousal: value in range [-1.0, 1.0]. It represents the degree of engagement (positive arousal), or disengagement (negative arousal).
- valence: value in range [-1.0, 1.0]. It represents the degree of pleasantness (positive valence), or unpleasantness (negative valence).
-
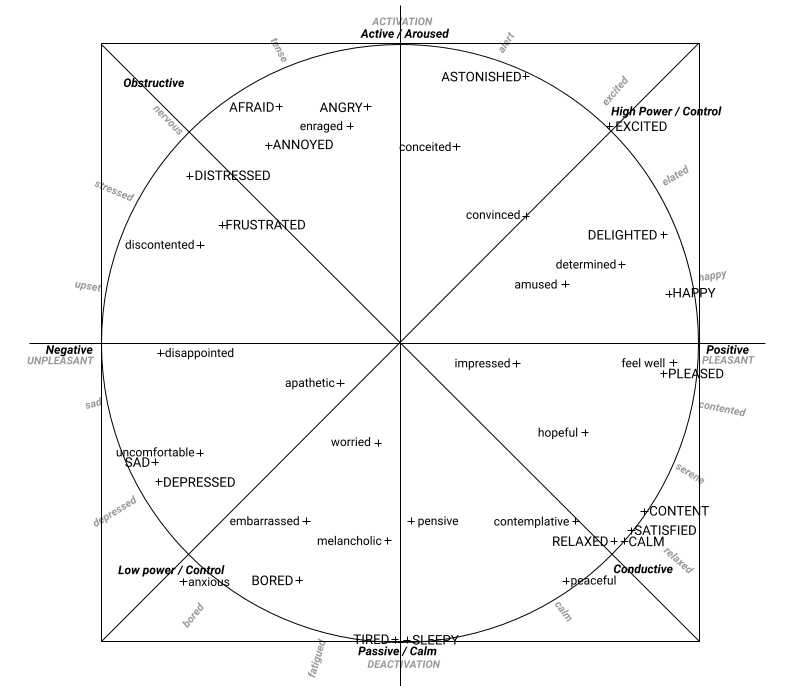
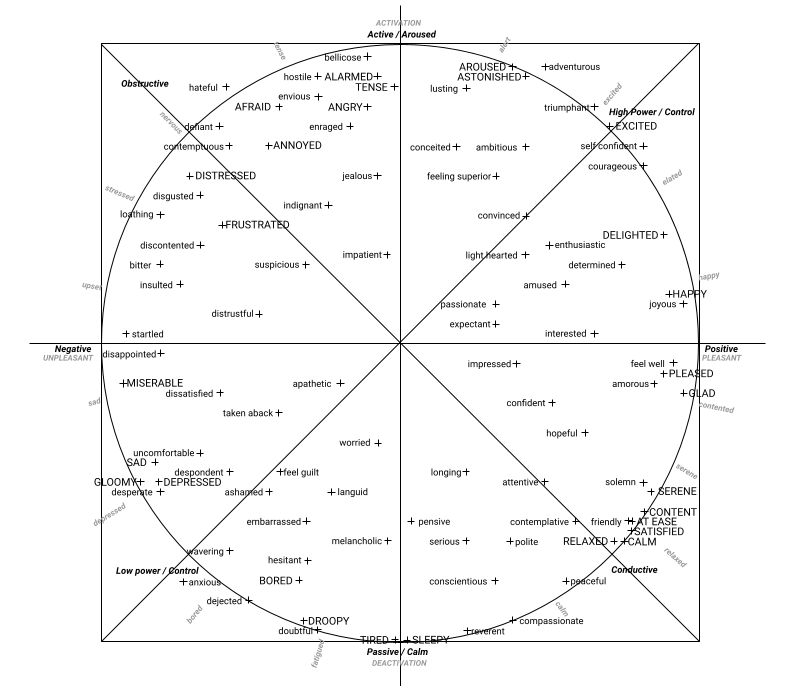
affects38: An object containing the smoothened probabilities of the 38 affects in range [0.00, 1.00]:
Afraid Amused Angry Annoyed Uncomfortable Anxious Apathetic Astonished Bored Worried Calm Conceited Contemplative Content Convinced Delighted Depressed Determined Disappointed Discontented Distressed Embarrassed Enraged Excited Feel Well Frustrated Happy Hopeful Impressed Melancholic Peaceful Pensive Pleased Relaxed Sad Satisfied Sleepy Tired
-
affects98: An object containing the smoothened probabilities of the 98 affects in range [0.00, 1.00]:
Adventurous Afraid Alarmed Ambitious Amorous Amused Wavering Angry Annoyed Anxious Apathetic Aroused Ashamed Worried Astonished At Ease Attentive Bellicose Bitter Bored Calm Compassionate Conceited Confident Conscientious Contemplative Contemptuous Content Convinced Courageous Defient Dejected Delighted Depressed Desperate Despondent Determined Disappointed Discontented Disgusted Dissatisfied Distressed Distrustful Doubtful Droopy Embarrassed Enraged Enthusiastic Envious Excited Expectant Feel Guilt Feel Well Feeling Superior Friendly Frustrated Glad Gloomy Happy Hateful Hesitant Hopeful Hostile Impatient Impressed Indignant Insulted Interested Jealous Joyous Languid Light Hearted Loathing Longing Lusting Melancholic Miserable Passionate Peaceful Pensive Pleased Polite Relaxed Reverent Sad Satisfied Selfconfident Serene Serious Sleepy Solemn Startled Suspicious Taken Aback Tense Tired Triumphant Uncomfortable
- quadrant: A string representing one of the four quadrants in the cirumplex model of affect ("High Control", "Obstructive", "Low Control", "Conductive", or "Neutral")
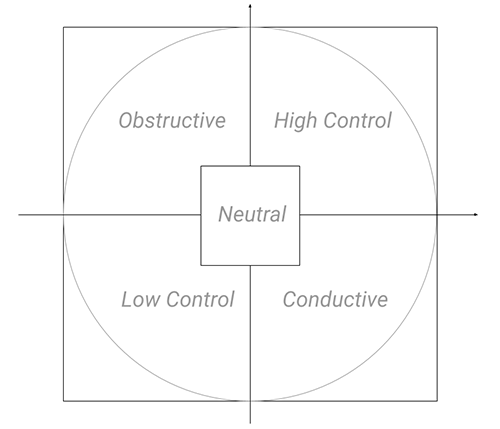
-
FACE_ATTENTION
FACE_ATTENTION initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.83};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_ATTENTION.name, config)
-
config:
- smoothness: Number, default 0.83. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response. Set it to 0 (zero) if you need the raw signal.
- riseSmoothness: Number. Same as smoothness, but is applied only when attention value is increasing. By default it has the same value as smoothness parameter.
- fallSmoothness: Number. Same as smoothness, but is applied only when attention value is decreasing. By default it has the same value as smoothness parameter.
FACE_ATTENTION registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_ATTENTION.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face attention result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_ATTENTION event.detail:
const FACE_ATTENTION_EVENT = {
output: {attention: Number}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the face attention prediction
- attention: filtered value (smoothened) in range [0.0, 1.0]. A value close to 1.0 represents attention, a value close to 0.0 represents distraction.
Note: after the first face prediction, this module will continue to emit events even though there are no frames or faces to analyze. In this case, attention events will still be emitted, but at a slower rate (about a half of the previous speed rate). So if you intend to accumulate and average the results, remember to sample first.
FACE_WISH
FACE_WISH initialization:
const config = {smoothness: 0.8};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_WISH.name, config)
-
config:
- smoothness: Number, default 0.80. Value should be in range [0,1). A value near 1 provides greater smoothing and slower response (longer delay). Lower values provide lesser smoothing but faster response.
FACE_WISH registration:
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_WISH.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face wish result', evt.detail);
});
FACE_WISH event.detail:
const FACE_WISH_EVENT = {
output: {wish: Number}
}
-
output: An object containing the output of the face wish prediction
- wish: filtered value (smoothened) in range [0, 1.0]. A value close to 0 represents a lower wish, a value close to 1.0 represents a higher wish.
ADVANCED TOPICS
General
- Do I need a license key to use MorphCast AI HTML5 SDK?
- Can I run multiple instances of the SDK within the same web page?
- Can I defer the download the SDK?
Camera stream
- How can I use a custom camera stream?
- How can I use a video stream intead of camera?
- How can I use an external IP camera as a custom source?
- How can I rotate the camera source?
- How can I crop the camera source?
- Can I get camera frames acquired by the library?
- Can I display the camera stream, with a higher resolution?
Single picture
- How can I use a custom picture instead of a camera stream?
- Is it possible to analyze single pictures in an Android/iOS App?
Alert plugin (MPH Tools)
- How to configure the alert plugin?
- Can I check the browser compatibility without showing the default Alert?
- Can I show a custom privacy Alert when the user is prompted for camera access?
- Do I need to warn the user before opening his camera device?
SDK in App
- How can I integrate MorphCast SDK in an Android App?
- How can I integrate MorphCast SDK in an iOS App?
- How can I integrate MorphCast SDK in a Desktop App?
Output values
- How can I represent the values in output of the SDK (using charts, histograms, etc.)?
- How can I use the values in output of the SDK?
Video conferences
- Do I need a license key to use MorphCast AI HTML5 SDK?
Yes, it is necessary to have a license key to use MorphCast AI HTML5 SDK.
You can easily autonomously generate it by filling this form and you will receive it by email in 2 minutes.
- Can I run multiple instances of the SDK within the same web page?
No, you can load only one instance of the SDK. Multiple instances in parallel are currently not supported and could lead to an unpredictable behaviour.
- Can I defer the download the SDK?
Instead of downloading the SDK automatically using the HTML <script> Tag, you can postpone it by using the document.createElement("script") JavaScript method.
See an example of implementation here.
- How can I use a custom camera stream?
The following utility snippet explains how to create a custom source.
You don’t need to open a camera stream, the SDK does it. In case you need to use a custom stream, follow the instructions. Remember that start-stop is already managed by the SDK.
<script>
const myCamera; // Your actual camera object;
const customSource = {
// The getFrame methods must return a promise resolved with the ImageData of the currentFrame.
// maxSize = Max size in px of the larger side of the frame. You should scale the image yourself before resolving it (optional).
getFrame(maxSize) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve(myCamera.getFrame().toImageData());
});
},
// resume the camera stream (can be an empty function)
start() {
},
// stop the camera stream (can be an empty function)
stop() {
},
// return the status of the camera Stream.
get stopped() {
}
};
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.source(customSource)
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load().then(({ start }) => {
start();
});
</script>
To create a custom stream using the Camera stream, you can use this ready-to-use function.
- How can I use a video stream intead of camera?
Here, there are a couple of ready-to-use functions you can use to create a custom source object using a video as an input.
By specifiying an intermediary HTMLVideoElement object, frames are grabbed from there and you have the full playback control:
const customSource = CY.createSource.fromVideoElement(document.getElementById("videoId"));
CY.loader()
.source(customSource)
// etc...
Otherwise, by providing a video URL, frames are grabbed from a video element automatically created and internally managed by the SDK:
const customSource = CY.createSource.fromVideoUrl("https://localhost/test.mp4");
CY.loader()
.source(customSource)
// etc...
- How can I use a custom picture instead of a camera stream?
As exposed in the following snippet, you need to pass each picture as an ImageData object, by calling:
customSource.analyzeFrame(...);
Note: for a synchronous analysis, you have to wait for the event result from the SDK before passing the next picture.
You can see a complete implementation using URLs to images, here.
<script>
let crtImgData;
let resolver;
const customSource = {
/*
frame producer
*/
analyzeFrame(imageData) {
if (resolver) {
resolver(imageData);
resolver = null;
} else {
crtImgData = imageData;
}
},
/*
frame consumer
*/
getFrame(...args) {
if (crtImgData) {
const p = Promise.resolve(crtImgData);
crtImgData = null;
return p;
} else {
return new Promise(res => resolver = res);
}
},
start() { },
stop() { },
get stopped() { }
};
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.source(customSource)
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name, {multiFace: true}) // disables tracker to enable one-shot analysis
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_EMOTION.name)
.load().then(({start, stop}) => {
start();
}).catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
/* This event is called after each face emotion analysis */
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_EMOTION.eventName, (evt) => {
// It's better to use raw output for one-shot photo analysis.
// This output is not documented because it should not be used in the normal scenario and could change in the future.
console.log(CY.modules().FACE_EMOTION.eventName, evt.detail.output.rawEmotion);
customSource.analyzeFrame(/* here, your next ImageData you want to process */);
});
customSource.analyzeFrame(/* here, the FIRST ImageData you want to process */);
</script>
- How can I use an external IP camera as a custom source?
No browser natively supports RTSP streaming, that is, you cannot simply put a video tag on an HTML5 page and play the RTSP streaming.
Instead, the usual approach is to use a proxy or a streaming server to convert the RTSP stream into something readable by the browser, eg. HLS or DASH.
- How can I rotate the camera source?
The following utility snippet explains how to create a custom source to rotate camera.
You can see it running here.
<script>
function initRotation({ width, height }) {
const rotationCanvas = document.createElement('canvas');
let rotationCtx = rotationCanvas.getContext('2d');
rotationCanvas.width = height;
rotationCanvas.height = width;
rotationCtx.rotate(Math.PI / 2);
rotationCtx.translate(0, -height);
return rotationCtx;
}
const tmpCanvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const tmpCtx = tmpCanvas.getContext('2d');
function toCanvas(imageData) {
tmpCanvas.width = imageData.width;
tmpCanvas.height = imageData.height;
tmpCtx.putImageData(imageData, 0, 0);
return tmpCanvas;
}
let rotationCtx;
let firstTime = true;
const camera = CY.createSource.fromCamera();
const customSource = {
getFrame(...args) {
const frameP = camera.getFrame(...args);
return frameP.then((imageData) => {
if (firstTime) {
rotationCtx = initRotation(imageData);
firstTime = false;
}
rotationCtx.drawImage(toCanvas(imageData), 0, 0);
return rotationCtx.getImageData(0, 0, imageData.height, imageData.width);
});
},
start() {
return camera.start();
},
stop() {
return camera.stop();
},
get stopped() {
return camera.stopped;
}
};
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.source(customSource)
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load().then(({ start }) => {
start();
});
</script>
- How can I crop the camera source?
The following utility snippet explains how to create a custom source to crop frames, e.g. to focus the detector on a specific area.
You can see it running here.
// Define here your crop region !
Crop = {
x:0,
y:0,
w:100,
h:100
};
// Define here your crop region !
const cropCanv = document.createElement('canvas');
const cropCanvCtx = newCan.getContext('2d');
const tmpCanvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const tmpCtx = tmpCanvas.getContext('2d');
function crop(ctx, x, y, w, h) {
const imageData = ctx.getImageData(x, y, w, h);
cropCanv.width = w - x;
cropCanv.height = h - y;
cropCanvCtx.putImageData(imageData, 0, 0);
return cropCanvCtx.getImageData(0,0,cropCanv.width,cropCanv.height);
}
function toCanvasCtx(imageData) {
tmpCanvas.width = imageData.width;
tmpCanvas.height = imageData.height;
tmpCtx.putImageData(imageData, 0, 0);
return tmpCtx;
}
const camera = CY.createSource.fromCamera();
const customSource = {
getFrame(...args) {
const frameP = camera.getFrame(...args);
return frameP.then((imageData) => crop(toCanvasCtx(imageData), Crop.x, Crop.y, Crop.w, Crop.h));
},
start() {
return camera.start();
},
stop() {
return camera.stop();
},
get stopped() {
return camera.stopped;
}
};
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.source(customSource)
.load().then(({ start }) => {
start();
});
- Can I get camera frames acquired by the library?
You can use an event listener and attach the CAMERA event to a canvas:
const ctx = document.getElementById('canvas').getContext('2d');
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().CAMERA.eventName, (evt) => {
const imageData = evt.detail;
ctx.canvas.width = imageData.width;
ctx.canvas.height = imageData.height;
ctx.putImageData(imageData, 0, 0);
});
Note: camera stream has been sampled and frames resized
- Can I display the camera stream, with a higher resolution?
You can attach directly to the camera stream, before frames are sampled and resized by the library:
const video = document.createElement('video');
video.setAttribute('muted', '');
video.setAttribute('playsinline', '');
// fix for ios 11
video.style.position = 'absolute';
video.style.width = '0';
video.style.height = '0';
document.body.appendChild(video);
const constraints = {audio:false,video: { width: 1920, height: 1080 };
loader = CY.loader()
.source(CY.createSource.fromCamera({constraints, video}))
...
Note: the SDK will internally down-scale the input, eg. to 320px.
If you want also the SDK to process a greater input, you have to set the maxInputFrameSize parameter to a greater value in two places, that is both in the configuration of the SDK and in the configuration of the FACE_DETECTOR module:
E.g.
...
loader = CY.loader().
.source(CY.createSource.fromCamera({constraints, video}))
.maxInputFrameSize(1920)
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name, {maxInputFrameSize: 1920})
...
Instead, if you want to manually sample camera frames at the same frequency of the library, you have to use a custom camera source and grab two frames at distinct resolutions (respectively, one for the library and one in HD for displaying):
const camera = CY.createSource.fromCamera();
const customSource = {
getFrame(...args) {
camera.getFrame(/* full HD constraints */).then((imageData)=>{
// put imageData into a full HD canvas
}); // frame full HD
return camera.getFrame(...args); // frame for the library
},
start() {
return camera.start();
},
stop() {
return camera.stop();
},
get stopped() {
return camera.stopped;
}
};
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.source(customSource)
.load().then(({ start }) => {
start();
}).catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
- Do I need to warn the user before opening his camera device?
Actually, it is not necessary to ask the user for consent, because the frames are processed locally on the browser and no personal data is sent to any server. But we highly recommend to explain to the user why the camera request is triggered and how the MorphCast SDK technology protects privacy.
You can use the alert plugin described below to automatically do this for you.
- How to configure the alert plugin?
Alert plugin (Mphtools) allows you to automatically check for browser compatibility and show a privacy Alert when the user is prompted for camera access. You can choose which settings to enable, by adding them in the mphtools-feature meta tag:
<head>
<meta name="mphtools-feature" content="allowCompatibilityClose, compatibilityUI, cameraPrivacyPopup, compatibilityAutoCheck">
</head>
This is the list of settings:
- allowCompatibilityClose: shows the close button in the compatibility Alert
- compatibilityUI: checks if the browser is compatible with MorphCast SDK and shows a graphic Alert in case the browser is incompatible.
- cameraPrivacyPopup: shows a privacy Alert every time the user is prompted to grant the permission to camera access
- compatibilityAutoCheck: checks immediately the browser compatibility when the page is loaded, instead of waiting the camera request
- Can I check the browser compatibility without showing the default Alert?
Yes. If you are using the Alert plugin (mphtools), you can disable the automatic check for browser compatibility and the automatic visualization of the full-screen message. You need just to remove the compatibilityUI setting in the mphtools-feature meta tag:
<head>
...
<meta name="mphtools-feature" content=""> // instead of content="compatibilityUI"
</head>
Then, you can check by yourself the browser compatibility:
switch(MphTools.Compatibility.check()){
...
MphTools.Compatibility.status.FB_AND:
break;
MphTools.Compatibility.status.COMPATIBILE:
break;
MphTools.Compatibility.status.INCOMPATIBLE:
break;
...
}
The returned status can be:
- SF_IOS: 'not_sf_ios' - Case in iOS but different browser than Safari
- FB_IOS: 'fb_ios' - Case in iOS inside FaceBook App
- FB_AND: 'fb_and' - Case in Android inside FaceBook App
- IG_IOS: 'ig_ios' - Case in iOS inside Instagram App
- IG_AND: 'ig_and' - Case in Android inside Instagram App
- LK_IOS: 'lk_ios' - Case in iOS inside Linkedin App
- WC_AND: 'wc_and' - Case in Android inside WeChat App
- WC_IOS: 'wc_ios' - Case in iOS inside WeChat App
- INCOMPATIBLE: 'incompatbile' - Case with general Incompatibility
- COMPATIBLE: 'compatible' - this is the only status which grants compatibility
- Can I show a custom privacy Alert when the user is prompted for camera access?
Yes. Instead of the default privacy Alert, you can write your custom privacy message and use the integration instructions below.
Using the alert plugin (mphtools), add the cameraPrivacyPopup setting in the mphtools-feature meta tag. Then, provide an implementation to the callback methods in the customPrivacyAlert object to show or hide your custom alert, and apply the mphtools config before loading the SDK:
<head>
...
<meta name="mphtools-feature" content="compatibilityUI, cameraPrivacyPopup, compatibilityAutoCheck">
</head>
<body>
...
<script src="https://sdk.morphcast.com/mphtools/v1.0/mphtools.js"></script>
<script src="https://ai-sdk.morphcast.com/v1.14/ai-sdk.js"></script>
<script>
const customPrivacyAlert = {
show() {
// write here the code for showing your custom Alert, when asking the camera to the user
},
hide() {
// for hiding your custom Alert
},
cameraDenied(){
// for showing an alternative message after camera has been denied by the user
}
};
MphTools.config({customPrivacyAlert:customPrivacyAlert});
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load()
.then(({ start, stop }) => start());
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Face detector result', evt.detail);
});
</script>
...
</body>
- How can I integrate MorphCast SDK in an Android App?
The following steps are shown in these templates. A working App example can be found here
- Create an Activity with a WebView inside.
- Configure the WebView to enable Javascript and to add a JavascriptInterface.
- Set the WebView URL to this page: webview URL (to import later on your server or inside the assets of the app)
- Declare the JavascriptInterface in order to have the functions getFrameFromApp(int maxSize) and onDataFromMphSdk(String type, String value).
In this way you will have a working bidirectional communication channel between the Javascript in the webview and the Android application.
- The Javascript in the html page will ask for a frame encoded in Base64 to be returned invoking the getFrameFromApp(int maxSize) method of the JavascriptInterface.
- The results of the Mph-SDK will be passed to the app through the method onDataFromMphSdk(String type, String value) of the JavascriptInterface.
- How can I integrate MorphCast SDK in an iOS App?
The following steps are shown in these templates. A working App example can be found here
- Create an app UIViewController with a WKWebView inside.
- Set the WebView URL to this page: webview URL (to import later on your server or inside the assets of the app)
- Instantiates and configure a WKUserContentController with two MessageHandlers: camera and data.
- Extend the ViewController with a WKScriptMessageHandler which contains the function used as a callback for the MessageHandlers.
In this way you will have a working bidirectional communication channel between the Javascript in the webview and the iOS application.
- The Javascript in the html page will ask through the MessageHandler (with WKScriptMessage.name == "camera") to return a frame encoded in Base64.
- The app should send the frame to the Javascript with the webview method webView.evaluateJavaScript("resolveFrame('([base64Image])')", completionHandler: nil) where [base64Image] is the string Base64 encoded of the frame. The results of the Mph-SDK will be passed to the app through the MessageHandler (with WKScriptMessage.name == "data")
- Is it possible to analyze single pictures in an Android/iOS App?
Yes, you can use the same instructions above.
We only suggest to update the html page where your App's webview target to, as follows.
As you are planning to analyze images not belonging to a video or camera stream, it is convenient to disable the tracker in the SDK. To disable the tracker, it is sufficient to load the module FACE_DETECTOR with the following config:
const config = {multiFace: true};
loader = CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name, config)
You can see an example here:
- How can I integrate MorphCast SDK in a Desktop App?
If your App is written in a native language (such as C, C++, Go, Java, or Python), you can use the Chromium Embedded Framework (CEF), or CefSharp in case of C# or VB.NET App.
If you are using Electron to build a cross-platform Desktop App, you can integrate the SDK following the example in our GitHub repository, here.
- How can I represent the values in output of the SDK (using charts, histograms, etc.)?
There are some ready-to-use graphical demo examples in our GitHub repository, here.
For example, you can plot detected emotions on a 2D space using the emotional spectrum model:

- How can I integrate the SDK with Zoom?
You can follow the official documentation. Here the main steps:
To join a meeting from web
- Import Zoom Web SDK
- Create a JWT Application in Zoom Marketplace. This will give you an API Key and a secret that will be used in the WEB SDK. You can import their example project and run it locally.
After you complete all these steps, you should be able to join any meeting created previously.
To create a meeting
- Authenticate with your zoom account
- Get the access TOKEN
- Create a meeting using the ZOOM APIs.
In order for zoom login to work you also need to create an OAuth App in Zoom Marketplace. After you get the authentication TOKEN, you will be able to use this method to create a meeting.
- How can I use the SDK in video-conferences?
Block diagram of an example for e-Learning
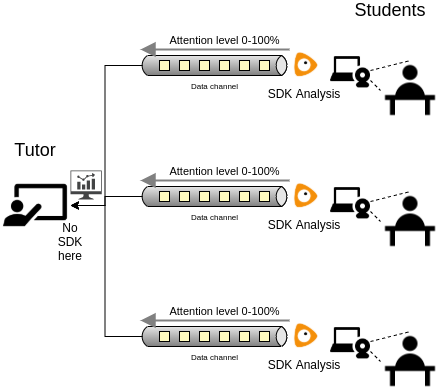
We encourage to analyze each face of each participant by his/her camera stream, sending the detected data to the other participants or to one or more specific participants using your conference communication channel. This solution is more scalable, you will have more accuracy in analysis independently of the network bandwidth and even if the participant disables the video communication.
Here, an example about how to integrate the SDK with Twilio service, for creating a video-call platform with emotion recognition, according to the circumplex model of affect.
Troubleshooting
Possible issues/error messages
- "You cannot load this SDK from an HTML page in your local file system. Please, serve this web page using a cloud or local web server."
- "Incorrect source path. SDK script is downloaded from a third-party server or proxy. Unpredictable behaviour can occur."
Solutions
"You cannot load this SDK from an HTML page in your local file system. Please, serve this web page using a cloud or local web server."
For security reasons, it is generally not recommended to open an HTML page in the local file system directly via browser. In fact, browsers become more and more stringent in making web applications work in that way, and some features are not available (e.g. root relative links, ajax and cors, cookies and local storage, service workers, etc.). So we cannot grant that MorphCast SDK will work correctly now or in the future, when loaded by a page with a "file://" URI scheme.
To work around these limitations we suggest two alternative ways:
- put the page on a cloud web server;
- or, serve HTML pages using a local web server.
"Incorrect source path. SDK script is downloaded from a third-party server or proxy. Unpredictable behaviour can occur."
The SDK must always be downloaded from the url indicated in the getting started snippet.
It is not allowed to autonomously distribute the SDK from servers not authorized by us even through a proxy server. Refer to the "Use of the Service" section of our Terms of Use.
Requirements
Minimum Requirements:
- Wasm Support
- Javascript Enabled Browser
-
Updated Browser and OS:
- Edge 16+ for Windows 10+
- Chrome 67+ for Android 5+, or Windows 7+, macOS 10.10+, Linux Ubuntu 14.04+, Debian 8+, openSUSE 13.3+, or Fedora Linux 24+
- Safari 11.3+ for iOS 11.3+, or macOS 10.12+
- Firefox 63+ for Windows 7+, macOS 10.9+, Linux (GTK+ 3.4, GLib 2.22, Pango 1.22, X.Org 1.0, libstdc++ 4.6.1)
KNOWN DEVICE ISSUES:
- iOS up to version iOS 11 doesn't support GetUserMedia.
- iOS up to version iOS 11.3 doesn't support the needed Wasm features.
- Microsoft Edge up to version 16 doesn't support Wasm.
- Microsoft Internet Explorer is not supported.
- Opera mini is not supported.
CAMERA:
- Mandatory: GetUserMedia Support
FACE_DETECTOR:
- Recommended: Wasm
- Mandatory: WebWorkers Support
OTHER MODULES:
- Recommended: WebGpu OR WebGl OR Wasm
- Mandatory for Wasm: WebWorkers Support
Change Log
1.14.14
- Fixed Wasm support for Safari 14+ (iOS and Mac OS)
1.14.9
- Added Affects output to FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE module
1.14.8
- Added check of correct input source
- Updated endpoints
- Added error message in case of incorrect source path of SDK
1.14.7
- Added some warnings
1.14.6
- Updated totalFaces output in FACE_DETECTOR event
1.14.5
- Security updates
- Minor bugfixes
1.14.4
- Updated endpoints
1.14.3
- Added parameter for enabling multi-face in FACE_DETECTOR module
- Added totalFaces output in FACE_DETECTOR event
1.14.2
- Added rise and fall smoothness parameters for FACE_ATTENTION module
1.14.1
- Added createSource facility for creating a custom source from Camera, VideoElement or URL
1.14.0
- Updated architecture to dynamically adapt the rate of analysis to available computing resources
- Added powerSave configuration parameter
1.13.0
- Updated FACE_DETECTOR module, increased working resolution
1.12.0
- Updated flow management of errors
- Updated endpoints
- Minor bugfixes
1.11.0
- Updated FACE_ATTENTION module
- Updated filters of FACE_AROUSAL_VALENCE, FACE_POSE, FACE_EMOTION modules
- Added filters to FACE_FEATURES module
- Added parameter for multi-face detection
- Added licenseKey interface
1.10.0
- Added MphTools plugin for compatibility check and privacy alert
- Updated FACE_WISH module
1.9.0
- Updated architecture for loading modules
- Added FACE_WISH module
1.8.6
- Added mostConfident output to FACE_GENDER event
- Minor bugfixes
1.8.5
- Fixed issue with Safari 13+ (for iOS and Mac OS)
- Security updates
1.8.4
- Updated endpoints for morphcast.cn (China)
1.8.3
- Minor bugfix related to configuration of modules
Code interface
MorphCast SDK defines this global object: CY
Example:
CY.loader()
This object contains all the methods and classes listed below.
loader
Creates the SDK instance
Note: creating multiple instances of the SDK is not supported.
AiSdkBuilder:
object for managing the configuration and loading of the SDK instance
CY.loader()
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load()
.then(({ start, stop, terminate }) => start());
modules
Returns all the AI-SDK module objects, each one with the following structure: { name: 'moduleName', event: 'eventName', specificEventA:'aSpecificEventOfTheModule'}
{CAMERA, FACE_DETECTOR, FACE_BASE, FACE_AGE, FACE_EMOTION, FACE_FEATURES, FACE_GENDER, FACE_POSE, SMART, FRUIT, etc..}:
CY.loader().addModule(CY.modules().MODULE.name);
// ...
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().MODULE.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log('Result', evt.detail);
});
createSource
Factory tool to create a custom source object for MorphCast SDK.
const cameraSource = CY.createSource.fromCamera({constraints, video});
const customSource = CY.createSource.fromVideoElement(document.getElementById("videoId"));
const customSource = CY.createSource.fromVideoUrl("https://localhost/test.mp4");
Camera factory method to get a source, able to grab images from device camera. Internally, it uses getUserMedia.
(Object
= {})
custom configurations
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
config.constraints Object
(default {audio:false,video:true})
|
getUserMedia constraints |
config.video HTMLVideoElement
(default document.createElement('video'))
|
video tag that will receive getUserMedia stream as srcObject |
config.flip Number
(default 0)
|
Flips the acquired frame clockwise 90 degrees * flip value.
|
Camera:
source object for MorphCast SDK
const cameraSource = CY.createSource.fromCamera({constraints, video});
cameraSource.start().then(() => {
const maxSize = 640; // Optional
cameraSource.getFrame(640).then(imageData => console.log(imageData));
};)
Factory method to get a source, able to grab frames from the specified HTMLVideoElement object.
(any)
HTMLVideoElement object
Object:
source object for MorphCast SDK
const customSource = CY.createSource.fromVideoElement(document.getElementById("videoId"));
CY.loader()
.source(customSource)
// etc...
Factory method to get a source, able to grab frames from the video media resource specified in the URL. A video element is created and managed internally.
(any)
String containing the URL for the video resource
Object:
source object for MorphCast SDK
const customSource = CY.createSource.fromVideoUrl("https://localhost/test.mp4");
CY.loader()
.source(customSource)
// etc...
AiSdkBuilder
Object returned by the "CY.loader()" method. It is used to configure and load the SDK instance.
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.source(CY.getUserMediaCameraFactory().createCamera()) // Optional
.maxInputFrameSize(320) // Optional - Default 320px
.powerSave(1) // Optional - Default 0.4
.loadErrorHandler((err)=>console.error(err)) // Optional
.runErrorHandler((err)=>console.warn(err)) // Optional
.load() // Mandatory
.then(({ start }) => start());
window.addEventListener(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, (evt) => {
console.log(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.eventName, evt.detail);
});
Optional. Default: load all licensed modules
Adds a module that will be loaded
(any)
(Object
= {})
[{}]
Module configuration
AiSdkBuilder:
Sets the power save percentage for frame processing cycles, from 0 (0%) to 1 (100%). The rate of analysis per second will dynamically adapt to available computing resources. A higher power save factor means a lower CPU and GPU usage.
(number
= 0.4)
factor
AiSdkBuilder:
Sets a custom source that will be used to provide the SDK modules with images. If no custom source is specified, the internal source of the SDK will be used by default. The internal source only gets a 640x480 camera stream from the browser (or similar), in order to be compatible with most devices and browsers.
(Object)
Source of images to process
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
source.getFrame Function
|
getFrame(maxSize) should return the imageData to be processed resized to maxSize if defined. |
source.start Function
|
start() should start the acquisition process. Eg: call getUserMedia(...) |
source.stop Function
|
stop() should stop the acquisition process. |
source.stopped boolean
|
stopped should return true if the camera is currently stopped |
AiSdkBuilder:
Sets the down-scaling to perform to the input source, before passing frames to the SDK modules.
Normally, the internal source of the SDK gets a 640x480 camera stream from the browser, then frames are reduced to 320px by default. Aspect ratio is preserved.
The value set should be between 320 and 640, since up-scaling cannot be performed.
A higher value can be set only when using a custom source, as long as it does not exceed the size of the input.
(number
= 320)
target resolution for the greater dimension, in pixels
AiSdkBuilder:
Sets an handler for errors occurring while modules are loaded.
(Function
= (err)=>console.error(err))
handler the load error handler
AiSdkBuilder:
Sets an handler for errors occurring while processing frames in modules
(Function
= (err)=>console.warn(err))
handler the run error handler
AiSdkBuilder:
Sets and handler for module.process() rejected because the previous processing has not yet finished.
(Function
= (err)=>undefined)
handler the busy message
AiSdkBuilder:
Load all the added modules
To start, stop or unload the SDK, you can invoke the "start", "stop" and "terminate" methods returned by the promise, see the example below.
Promise<{start, stop, terminate}>:
let stopSDK, terminateSDK;
CY.loader()
.licenseKey("insert-here-your-license-key")
.addModule(CY.modules().FACE_DETECTOR.name)
.load()
.then(({ start, stop, terminate }) => {
stopSDK = stop;
terminateSDK = terminate;
start();
setTimeout(stopSDK, 10000); // SDK will be stopped after 10 seconds after loading
setTimeout(terminateSDK, 20000); // SDK will be unloaded after 20 seconds
});
Camera
Camera that uses GetUserMedia.
Note: it cannot be initialized with
Stops the camera stream.